One of the most important things when you want to operate a business in Indonesia is understanding the labor laws in this country. At the very least, you should be familiar with the basic rules in Indonesia Labor Law No. 13 of 20031 and the Job Creation Law No. 6 of 20232 with its derivative employment regulations to ensure your business compliance.
Here, we summarize some substantial rules to help you start a business in Indonesia.
Types of Employment Contracts
Indonesian labor law distinguishes between two types of contracts that form the basis of the employment relationship between the employer and the employee, namely:
1. Temporary Contract (PKWT)
PKWT is a temporary employment agreement limited to a maximum of five years. The agreement is applicable when written in Bahasa Indonesia. It is not possible to require a probationary period in the PKWT.
PKWT is extendable as long as the total duration of the PKWT and the extension does not exceed five years. At the end of the PKWT or extension, you will pay contract compensation equal to the length of service divided by 12, then multiplied by one month’s salary.
2. Permanent contract (PKWTT)
PKWTT is a continuous employment agreement with no time limit. The relationship between employer and employee will end through a termination (PHK) only, and the employer will provide severance pay. PKWTT is applicable in writing or verbally and may include a 3-month probation period.
Types of Jobs in Indonesia

Before hiring employees, you need to know the types of jobs in Indonesia:
1. Permanent Job: A full-time employment continuously performed by permanent employees based on a PKWTT.
2. Temporary Job: A job in one-time, seasonal, trial, or expected to be completed within five years, performed by temporary workers based on a PKWT.
3. Daily Irregular Job: A specific job that varies in time and volume, with wages paid based on employee attendance. The employee works for less than 21 days a month.
4. Flex Job: A job with flexible hours, such as remote and freelance.
5. Part-Time Job: A job with less than 7 hours a day and less than 35 hours a week.
6. Independent Contract: A job worked by contractors and paid on a lump sum basis according to the agreed project value.
7. Outsourcing: Specific works or services performed by a labor outsourcing company to users.
8. Expert Service: Works or services done by experts and consultants for their clients or companies.
Also Read: Employment Types in Indonesia: Contracts and Regulations
Female Workers Protection
You can recruit and employ women as part of your organization. However, you must comply with the regulations regarding female workers in Indonesia, including:
1. Protection
The Indonesia Labor Law prohibits you from employing female workers under 18 between 11:00 PM and 7:00 AM. Additionally, you may not employ pregnant women on night shifts between 11:00 PM and 7:00 AM if, according to a doctor’s statement, it endangers the health and safety of the employee or her fetus.
If employing women between 11:00 PM and 7:00 AM, you should provide nutritious food and drinks, maintain security and decency at the workplace, and provide transportation for the employees.
2. Maternity Leave
The Indonesia Labor Law grants female workers three months of maternity leave. However, according to the Maternal and Child Welfare Law, female employees can receive up to six months of maternity leave in abnormal circumstances, as evidenced by a doctor’s certificate.
The law also prohibits you from firing women who give birth. Instead, you should pay the employees’ entitlements, with 100% of their salary for the first to fourth months and 75% for the fifth and sixth months.
3. Menstrual Leave
The law also offers female workers who suffer pain on the first and second days of menstruation a 2-day off.
4. Breastfeeding Opportunities
You should provide reasonable opportunities for female workers to breastfeed their children if it needs to be done during working hours, for example, by giving a breastfeeding room at the workplace.
5. Equal Rights
Female employees should receive the same rights as male employees, such as wages, leave, and career development opportunities. No gender-related discrimination is allowed by national laws.
Occupational Health and Safety in Employment Regulations
The Indonesia Labor Law requires every employer to ensure occupational safety and health, morality and decency, and to treat employees with dignity, human values, and religious norms. For this reason, you need to implement an integrated occupational safety and health system with the company’s management system.
Employees can request a cessation of employment if the employer violates the above provisions, such as abuses, insults, or threatens employees or assigns a job that endangers their lives, safety, and health without an agreement in the contract.
Salary and Minimum Wages

The government sets the minimum wage every year as a guideline for each company in setting the lowest salary for its workers. It is unacceptable to set employee salaries below the local minimum wages (UMP and UMK).
Moreover, the minimum wage applies only to new workers with less than one year of service at the company. For employees with one year of service or more, salaries follow the wage structure and scale. Each company should apply a wage structure and scale according to the employee’s job classification.
Wages are generally set based on time units, such as hourly, daily, and monthly wages. In addition, wages can also be set based on production units. You should pay wages in Indonesian Rupiah (IDR).
Also Read: How KITAS Holder Can Legally Work in Indonesia?
Working Hours and Overtime
According to the Job Creation Law, the working hours are 7 hours a day and 40 hours a week (6-day workweek) or 8 hours a day and 40 hours a week (5-day workweek).
If you require employees to work beyond these hours, you must calculate the excess as overtime and pay the wages. The maximum overtime is 4 hours a day and 18 hours a week, not including overtime on holidays and weekly rest days.
Overtime pay depends on an hourly wage, which is 1/173 of the monthly salary. The method for calculating overtime wages is as follows:
Total hours | Overtime Pay(x Hourly Wage) | |||
Workday Overtime | Holiday Overtime | |||
| 6-day workweek | 6-day workweek (holidays fall on the shortest workday | 5-day workweek | ||
| 1 hour | 1,5 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 2 hours | 3,5 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 3 hours | 5,5 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 4 hours | 7,5 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| 5 hours | 10 | 10 | 10 | |
| 6 hours | 12 | 13 | 12 | |
| 7 hours | 14 | 17 | 14 | |
| 8 hours | 17 | 21 | 16 | |
| 9 hours | 21 | 25 | 19 | |
| 10 hours | 25 | 23 | ||
| 11 hours | 29 | 27 | ||
| 12 hours | 31 | |||
For example, the payment for 3 hours of overtime on a workday is 5,5x hourly wage.
In addition to paying overtime wages, you should provide food and drinks at least 1,400 kilocalories to employees working overtime for 4 hours or more.
Off-Day and Leave
1. Work Breaks
Employers must provide a break of at least half an hour after four hours of work. This break time does not belong to working hours. Employees are also entitled to a weekly rest of one day for a 6-day workweek and two days for a 5-day workweek.
2. Annual Leave
The government regulates the number of annual leave days with a minimum of 12 working days after the employee has worked continuously for 12 months. In addition to annual leave, certain companies may offer long rest or sabbatical leave.
3. Special Leave
The Indonesia Labor Law grants special paid leave to workers as follows:
- The employee is sick and unable to work according to a doctor’s statement (more than 12 months off)
- The employee gets married (3 days off)
- Female employees suffer pain on the first and second days of their menstrual period; the employee marries off, circumcises, or baptizes a child; the employee accompanies his wife for childbirth or miscarriage; the spouse, parent/in-law, or child/son-in-law passes away (2 days off)
- A family member living in one house with the employee passes away (1 day off)
- The employee performs obligations to the state, fulfills religious duties, carries out trade union duties with the employer’s approval, or undertakes educational assignments from the company (depending on the agreement)
Religious Holiday Allowance (THR)
The Government Regulation orders every employer to pay a THR or Religious Holiday Allowance before religious holidays such as Eid al-Fitr, Christmas, Nyepi, Vesak, and Chinese Lunar New Year. Each employee receives a THR corresponding to their religious holiday, amounting to one month’s wage for employees who have worked for one year or more.
If an employee has worked for more than one month but less than one year, they are entitled to a proportional THR, calculated using the formula: (length of service/12) multiplied by one month’s salary. Employees who have worked for less than one month are not entitled to THR.
According to the regulations, you should disburse the THR no later than seven days before the holiday. If you delay the payments, a 5% penalty applies without eliminating the obligation to pay the THR.
Social Security and Health Insurance
Another obligation of employers towards their employees is to register them as participants of the BPJS Ketenagakerjaan social security program and the BPJS Kesehatan health insurance and to ensure the payment of contributions or monthly premiums.
You should manage BPJS contributions, pay your portion, and deduct the remaining part from the employee’s payroll. The contribution portions are as follows:
| BPJS Program | Contribution (x monthly salary) | Employer portion | Employee portion |
| Work Accident Insurance | 0.24-1.74% | 0.24-1.74% | 0% |
| Death Insurance | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0% |
| Old Age Security | 5.7% | 3.7% | 2% |
| Pension | 3% | 2% | 1% |
| Health Insurance | 5% | 4% | 1% |
The maximum salary for calculating pension in 2024 is IDR 10,042,300, and for calculating health insurance is IDR 12,000,000.
In addition to registering employees and paying BPJS premiums, you should report employee participation data through the SIPP Online system. If you neglect the above regulations, you may face administrative sanctions, such as warnings, fines, restrictions on permits and public services, and even criminal penalties of up to 8 years in prison or fines up to Rp 1 billion.
Also Read: How to Register Employee with BPJS Ketenagakerjaan
Income Tax Withholding
As the income provider for your employees, you will calculate and withhold their income tax under tax regulations. There are two types of employee income tax: PPh 21 for resident taxpayers and PPh 26 for non-resident taxpayers. Afterward, you remit the withheld tax and report it online via the e-Bupot 21/26 application.
Read about Income Tax in Indonesia for Foreign Businesses!
Termination of Employment (PHK)

Although discontinuing employment is the last option, sometimes you cannot avoid it. If you have to do so, you need to reduce the legal risk action by employees. You should ensure that the reasons for PHK are allowed by the regulations and that the process runs correctly.
1. Outlaw Reasons for PHK
You are not allowed by law to terminate employment for these reasons:
- The employee cannot work due to illness based on a doctor’s certificate and does not exceed 12 months.
- The employee is fulfilling obligations to the state according to legal regulations.
- The employee is performing religious duties as required by their religion.
- The employee is getting married.
- The employee is pregnant, giving birth, having a miscarriage, or breastfeeding their baby.
- The employee has a blood relation or marital connection with another employee in the same company.
- The employee is a member or official of a trade union and engages in activities after work or during working hours with the employer’s agreement.
- The employee reports the employer to the authorities for criminal acts.
- The employee has differences of beliefs, religion, political views, ethnicity, skin color, social class, gender, physical condition, or marital status.
- The employee is permanently disabled or sick due to a work accident (the recovery time is uncertain by the doctor’s statement).
If you do so, the PHK is considered null and void, and you must re-employ the sacked employees.
2. Legal Reasons for PHK
The Job Creation Law allows you to terminate a permanent contract for these reasons:
- Merger, consolidation, acquisition, or separation of the company, and the employee or employer is unwilling to continue the employment relationship.
- The company conducts efficiency measures due to losses.
- The company stops operating due to continuous losses over two years.
- The company closes due to force majeure.
- The company is under suspension of debt payment obligations.
- The company is bankrupt.
- PHK requested by the employee due to the employer: mistreating, grossly insulting, or threatening the employee; requiring the employee to perform actions contrary to the law; not paying wages on time for three consecutive months or more; failing to fulfill promised obligations; requiring the employee to perform work beyond the agreed terms; providing dangerous work that threatens life, safety, health, and morality not included in the employment agreement.
- A court decision stating that the employer did not commit the acts accused, and the employer can proceed with termination.
- The employee resigns voluntarily.
- The employee is absent for five consecutive working days or more without written explanation with valid evidence and has been called twice appropriately and in writing.
- The employee violates provisions in the employment agreement (PK), company regulations (PP), or collective labor agreement (PKB), and the employer has given a first, second, and third warning letter.
- The employee cannot perform work for six months due to detention by authorities for suspected criminal acts.
- The employee has prolonged illness or disability due to a work accident and cannot work for more than 12 months.
- The employee reaches retirement age.
- The employee dies.
3. Compensation for termination
Employers who terminate a contract must compensate the workers as follows:
- Severance pay depends on the employee’s tenure, with a multiplier based on years of service.
- Long service pay (UPMK) is similar to severance pay but with different multipliers.
- Separation pay is only available for a termination in which the employee is not eligible for severance pay and UPMK, such as resignation.
- Payment for unused annual leave, relocation expenses, and other benefits stipulated in the employment contract.
| Severance Pay | Long Service Pay | ||
| Tenure (year) | Payment(x monthly salary) | Tenure (year | Payment(x monthly salary) |
| < 1 | 1 | < 3 | 0 |
| 1 to < 2 | 2 | 3 to < 6 | 2 |
| 2 to < 3 | 3 | 6 to < 9 | 3 |
| 3 to < 4 | 4 | 9 to < 12 | 4 |
| 4 to < 5 | 5 | 12 to < 15 | 5 |
| 5 to < 6 | 6 | 15 to < 18 | 6 |
| 6 to < 7 | 7 | 18 to < 21 | 7 |
| 7 to < 8 | 8 | 21 to < 24 | 8 |
| ≥ 8 | 9 | ≥ 24 | 10 |
4. Termination procedures
If you intend to terminate permanent contracts, the initial step is notifying the workers or labor union by a letter containing the PHK reasons and the compensation. If they do not reply with a rejection letter, the PHK will be quick and easy. You will pay the compensation regulated by the Labor Law and report the PHK to the local Labor Office.
If the workers refuse the PHK, you have to negotiate with them. If the talks fail to conclude any agreement, you must report the matter to the local Labor Office for mediation. If the third-party mediation ends with no result, you should forward the case to the Industrial Relations Court.
Also Read: The Benefits of Using Payroll Outsourcing Services in Indonesia
Handling Personnel Administration with Payroll Software
Do not be stressed by the Indonesia Labor Law. Gadjian will help you manage your personnel administration, including salary, overtime, leave, social security of BPJS, religious holiday allowance, bonuses, income tax, wage structure and scale, and severance pay of termination.

Gadjian is the leading cloud-based payroll application and HR software providing faster automatic calculations. Forget about the manual payroll process, which is time-consuming and miscalculation-prone. Gadjian helps you avoid payroll errors as the online app uses an accurate and regularly tested algorithm.
Here are some advantages of using automatic payroll Gadjian:
- With autopilot payroll, your business will run efficiently. You have more time to focus on strategic tasks than wasting your time in the manual process of employee administration.
- Gadjian automatically calculates daily wages and prorated salaries as the app is ready to connect with attendance data.
- With the deduction hub, Gadjian prevents overpayments since the app will compute salary deductions and reduce the payslip correctly, including tax income PPh 21/26.
- Gadjian also computes overtime pay automatically based on the recent regulation so that you do not need to use the overtime formula figured in the table above.
- A payslip is available once the calculations are complete, and no manual recap is needed.
- Integration with payment apps and e-banking makes salary disbursement easy with just one click.
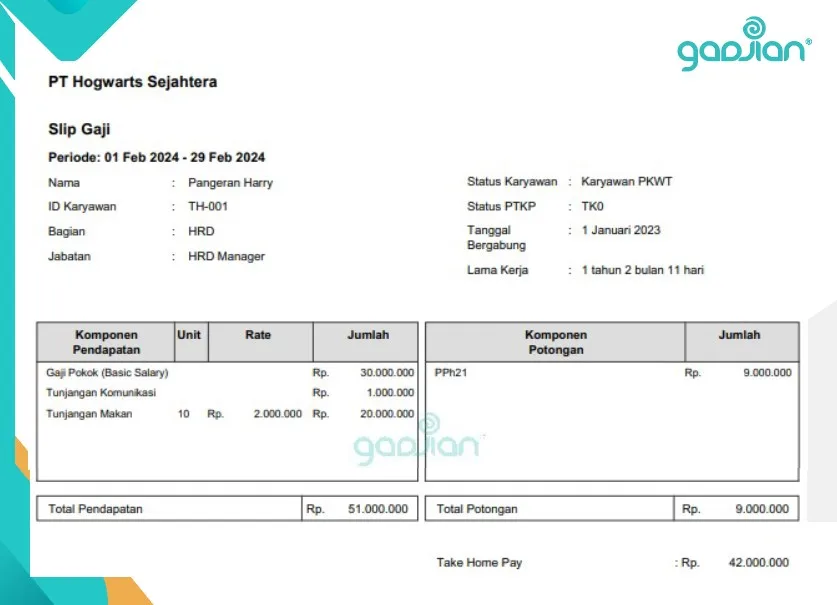
No time to manage payroll and payslip calculation? Leave them to us. Pegawe, an Indonesian payroll outsourcing service, will take over your tasks in payroll processing, BPJS social security registration and calculation, income tax withholding and filing, employee attendance tracking, salary disbursement, and contract termination.
You will be free from headaches. Just focus on the critical steps in your business. We will handle your payroll with Indonesia Labor Law compliance.

Pegawe provides professional service at an affordable budget. Whether you are starting your business or already have an established organization here, we can help you to be more efficient by managing your personnel administration.
Sumber




